Section 2 - Electricity
V = I * R
voltage = current * resistance
p = I * V
power = current * voltage
e = I * V * t
energy transferred = current * voltage * time taken
I = Q * t
current = charge * time taken
V = J / Q
voltage = joules / charge
mains supply = AC (alternating current) whereby the current is inverted very rapidly.
cell/battery = DC (direct current) whereby the current is always in one direction.
RMS (root mean square) = is a way to convert from peak voltage to shown voltage. The equation is:
RMS = peak AC voltage / √2
The following three graphs show the relationship between current and voltage.
As the voltage on a resistor increases, the current increases directly proportional to the voltage.
As the voltage on a filament lamp increases, the current increases but decelerates. This is because as current increases so does heat, the extra heat causes the atoms in the filament lamp to vibrate more, this creates more resistance thereby meaning less current can pass.
The current of a diode only increases when a certain set amount of voltage has been reached. After this point, current increases directly proportional to voltage.
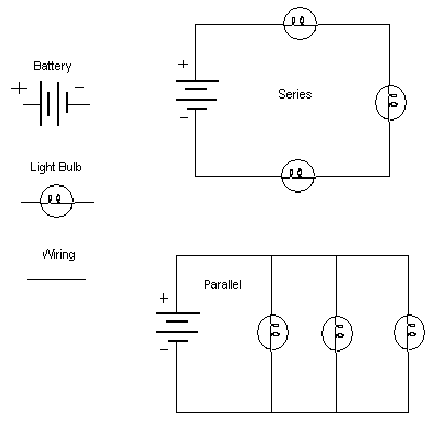
Benefits of series and parallel circuits :
Series:
- Energy efficient
- Less wiring
Parallel:
- Practical (can be independently controlled)
- If one part of the circuit was to break the entire circuit would not.
- Each closed loop would always receive the same amount of voltage so if for example, a lamp was added in parallel, all the lamps would remain bright while in a series circuit it would dim.
LDR = as light decreases so does the resistance
Thermistor = as heat decreases so does the resistance
The mains supply is 230V (RMS) with a peak voltage of 325V. Because of this, it is very dangerous if the mains charge is transferred to humans. Therefore, mains plugs have many safety features.
Safety features of mains plugs:
- The body is made of plastic, a good insulator.
- There is an earth pin to stop the plug from becoming charged. The earth pin is longer than the others so that it is always the first to make and the last to be broken.
- The cable is clamped to stop the wire from being pulled out.
- When there is no earth pin double insulation is used. This is where a layer of non-conductive material is wrapped around the body to stop it becoming charged.
- A fuse is placed on the live wire. When there is high current, enough temperature is created to melt the fuse, which breaks the circuit causing it to stop working.
Mains plugs wire colours:
- live - brown
- neutral - blue
- earth - green and yellow


No comments:
Post a Comment