ORGANIC CHEMISTRY:
Homologous Series - a family of compounds with similar chemical properties, a trench in physical properties, and the same general formula e.g. alkanes
Hydrocarbon - compounds that only contain hydrogen and carbon (Note. the word only is very important)
Saturated - contains the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible within the given number of carbons
Unsaturated - does not contain the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible because of double carbon-carbon bonds.
General formula - a molecular formula for a whole homologous series
Isomer - when two or more different compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural formula they are called isomers.
Alkanes:
General formula - CnH2n+2
Reactions involving alkanes:
Combustion - e.g CH4 + 2O2 —> CO2 + 2H2O
Incomplete combustion - e.g. 2CH4 + 3O2 —> 2CO + 4H2O
Methane reacts with bromine gas in the presence of UV light to form bromomethane and hydrogen bromide gas. This is a substitution reaction
CH4 + Br2 —> CH3Br + HBr
Alkenes:
General formula - CnH2n
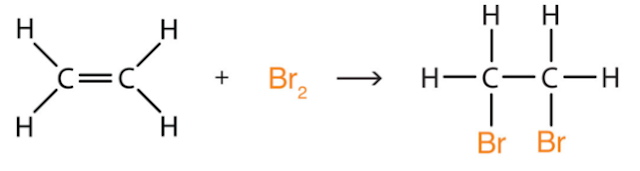
Alkenes have an addition reaction with bromine, the equations are:
e.g. CH2=CH2 + Br2 —> CH2BrCH2Br
This reaction is a classic test for alkenes. By passing an unknown organic compound through bromine water, if the orange bromine water is decolorised then there is a presence of a carbon-carbon double bond, a feature of alkenes. If, however, a alkane is present then the bromine water will remain orange and alkanes do not contain carbon-carbon double bonds.
Ethanol:
Manufacture of ethanol:
1. Hydration of ethene - steam and ethene is constantly passed over the catalyst of concentrated phosphoric acid at 300°C and at 60-70 atmospheres. This is a continuous flow process, which makes it very efficient. It also produces ethanol of far higher purity.
CH2=CH2 + H2O —> CH3CH2OH(g)
2. Fermentation - yeast is added to sugar or starch solution, left in warm conditions (30 - 40°C) and in absence of oxygen (anaerobic conditions). Enzymes convert the sugar into ethanol and CO2.
C6H12O6 —> 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
Dehydration of ethanol:
Ethanol vapour is passed across aluminium oxide (catalyst) with heat
CH3CH2OH —> CH2=CH2 + H2O
This also works for other types of alcohol
CH3CH2CH2OH —> CH3CH=CH2 + H2O



We also provide analytical services and laboratory services to our customers. Vat Brown 3
ReplyDelete